树,尤其是二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree => BST)是算法、数据结构领域重要的数据结构之一。
树是什么鬼 树(tree)是一种由节点(nodes)和无环向量(edges without having any cycle)构成的数据结构(通常是非线性的)。请参考这里
都有什么树 总的来说我们按照有序和无序的维度将树分为无序树和有序树。
无序树:树中任意节点的子节点之间没有顺序关系,这种树称为无序树,也称为自由树
有序树:树中任意节点的子节点之间有顺序关系,这种树称为有序树。
二叉树 :每个节点最多含有两个子树的树称为二叉树
B树 :概括来说是一个一般化的n叉搜索树,可以拥有多于2个子节点
霍夫曼树
和树相关的操作 由于二叉搜索树有着广泛的应用,所以这部分以二叉搜索树为例表述。
遍历(Travels)
中序(inorder)遍历
先序(preorder)遍历
后序(postorder)遍历
添加节点(Add node)
查找节点(Search node)
删除节点(Delete node)
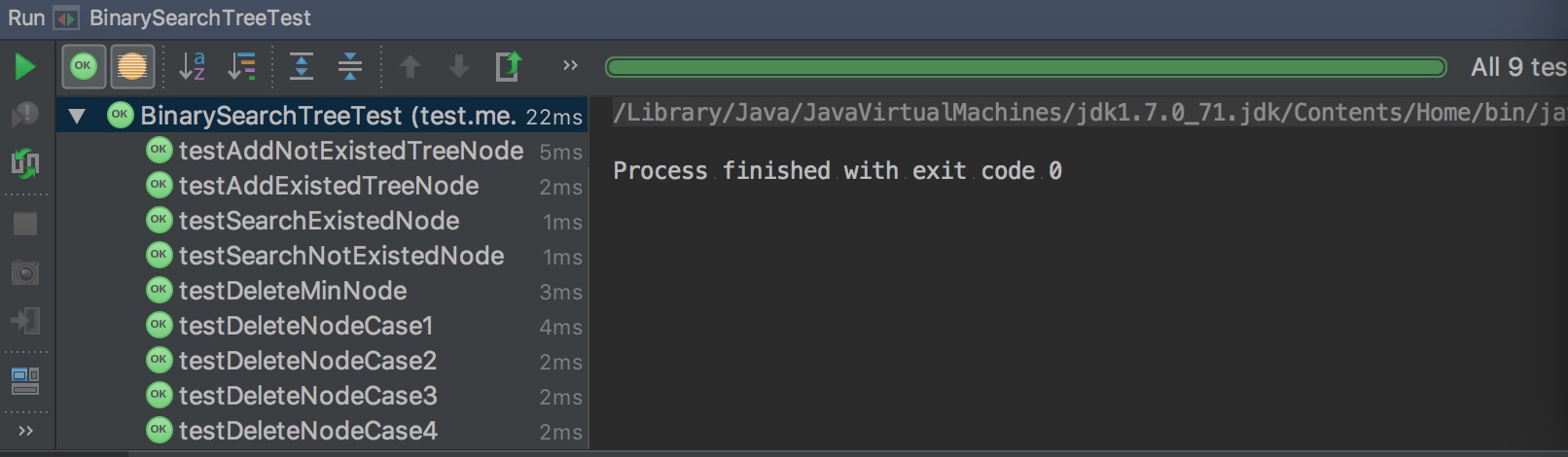
上面说得都是些比较抽象的内容,相信你一定已经按耐不住想撸一遍代码了。好!给你机会。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class TreeNode { TreeNode leftChild; TreeNode rightChild; int data; }
在进行遍历之前还有一个关键的步骤没有做,那就是构造树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class BinarySearchTree { TreeNode root; public BinarySearchTree () { } public TreeNode put (int value) { return put(this .root, value); } private TreeNode put (TreeNode root, int value) { if (root == null ){ this .root = new TreeNode (); this .root.data = value; return this .root; } int valueOfrootElement = root.data; if (value < valueOfrootElement){ root.leftChild = put(root.leftChild, value); }else if (value > valueOfrootElement){ root.rightChild = put(root.rightChild, value); }else { root.data = value; } return root; } }
是不是感觉上面的代码有些不舒服,对的,有代码强迫症的你肯定已经毛爪挠心了,不废话,消灭所有不合理的因素。这次从方法命名开始。
方法名中若不是简单的getter/setter 操作应当避免使用get/set作为方法名,以免引起不必要的误解。
改正后的版本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class BinarySearchTree { TreeNode root; public BinarySearchTree () { } public TreeNode addTreeNode (int value) { if (this .root == null ) { this .root = new TreeNode (value); } return addTreeNode(this .root, value); } private TreeNode addTreeNode (TreeNode root, int value) { if (root == null ){ return new TreeNode (value); } int valueOfrootElement = root.data; if (value < valueOfrootElement){ root.leftChild = addTreeNode(root.leftChild, value); }else if (value > valueOfrootElement){ root.rightChild = addTreeNode(root.rightChild, value); }else { root.data = value; } return root; } }
嗯,感觉舒服多了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public TreeNode searchNode (int value) { return searchNode(this .root, value); } private TreeNode searchNode (TreeNode root, int value) { if (root == null ){ return null ; } int rootValue = this .root.data; if (rootValue == value){ return root; } else if (value < rootValue) { return searchNode(root.leftChild, value); } else { return searchNode(root.rightChild, value); } }
上面的代码用到了inorder travels标准写法,递归(Reccurrence)调用查找方法。
我们实现了添加查找节点的方法,下一步就是实现删除节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public TreeNode deleteNode (int value) { return deleteNode(this .root, value); } private TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int value) { if (root == null ) { return null ; } int rootValue = root.data; if (value < rootValue) { root.leftChild = deleteNode(root.leftChild, value); } else if (value > rootValue) { root.rightChild = deleteNode(root.rightChild, value); } else { if (root.leftChild == null ) { return root.rightChild; } if (root.rightChild == null ) { return root.leftChild; } TreeNode newRootNode = findMin(root.rightChild); root.data = newRootNode.data; root.rightChild = deleteNode(root.rightChild, newRootNode.data); } return root; }
算法的细节就不解释了,稍微麻烦点的地方都有注释。
到了这里是不是觉得就可以打完收工了? No,No,No……
下附工程代码:gitHub